What’s New in XR & Android
GodotCon 2025 recap
A few weeks ago during GodotCon Boston 2025, David Snopek, Logan Lang and I gave the latest updates on the state of Android and XR for the Godot engine:
You can access the slides of the presentation.
Android & XR editor
Android editor
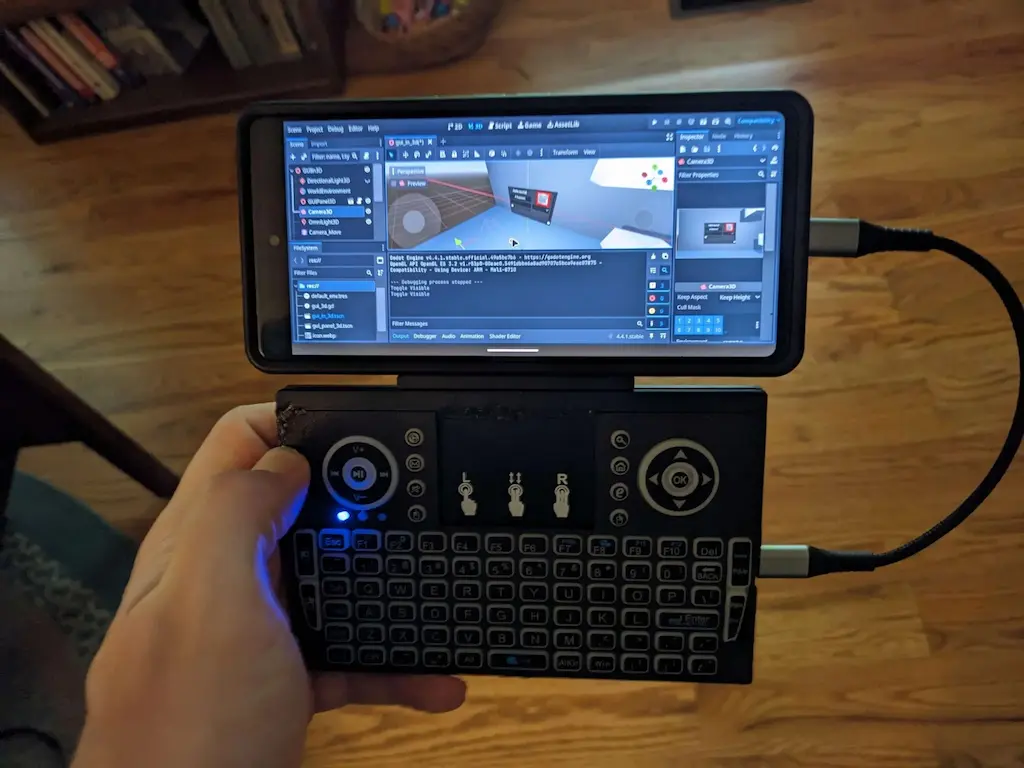
An update on the Android editor is long overdue. Since its release in 2023, the Android editor has been available on the Google Play store and on Godot’s download page with support for all Android devices (e.g.: phones, foldables, tablets, Chromebooks, and others).
Last fall, during GodotCon 2024, we announced that the Android editor had ~850K device installs from the Google Play store. Over the last 6 months, installs grew by another ~365K for a total of 1.2M device installs by GodotCon (Boston) 2025. This corresponds to over ~2000+ daily installs with over ~90K monthly active users.
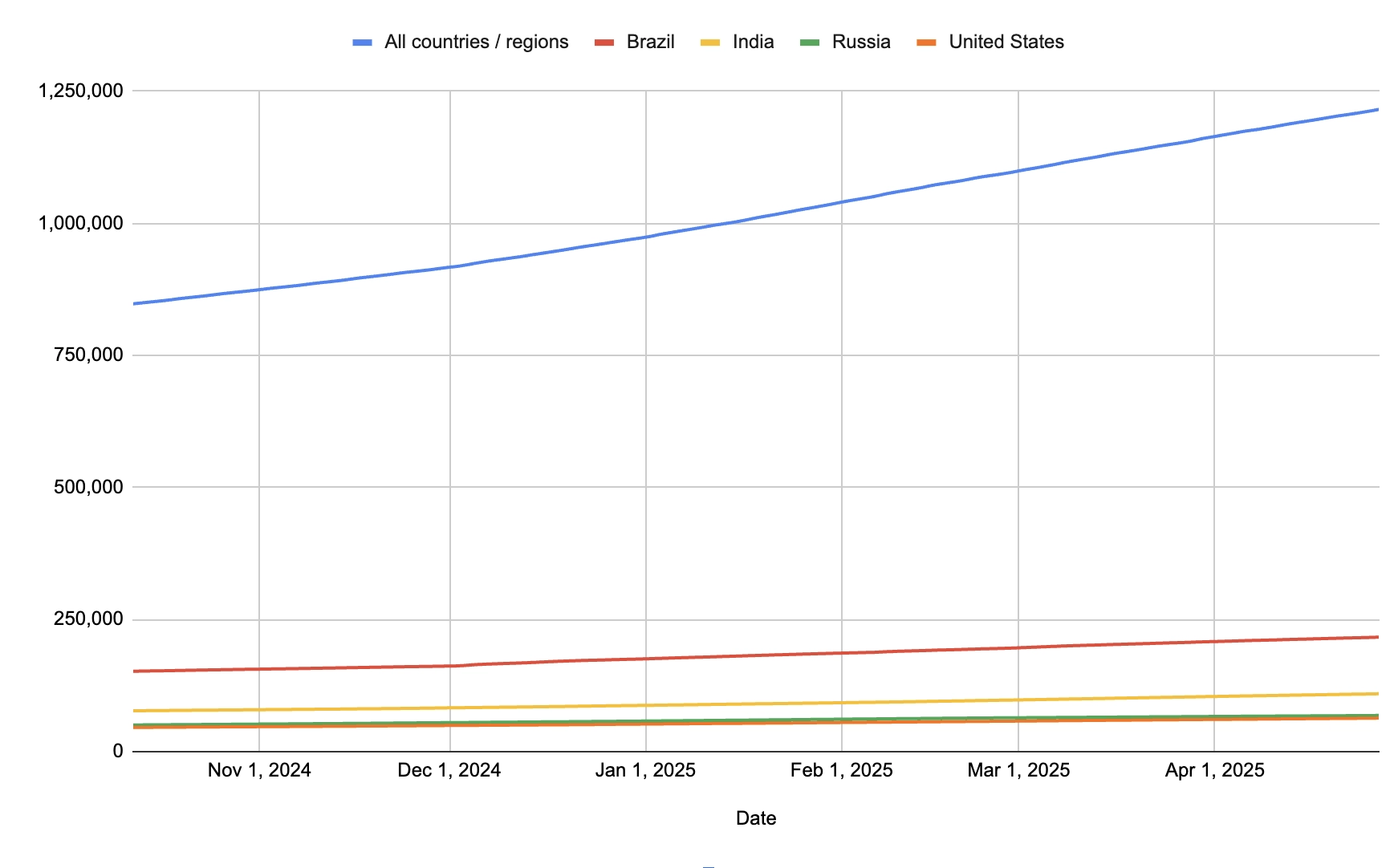
From the Google Play store data, we made a few interesting observations worth diving into.
Most installs are from Brazil + India
Brazil and India make up 26% of installs with 17% coming from Brazil and 9% coming from India.
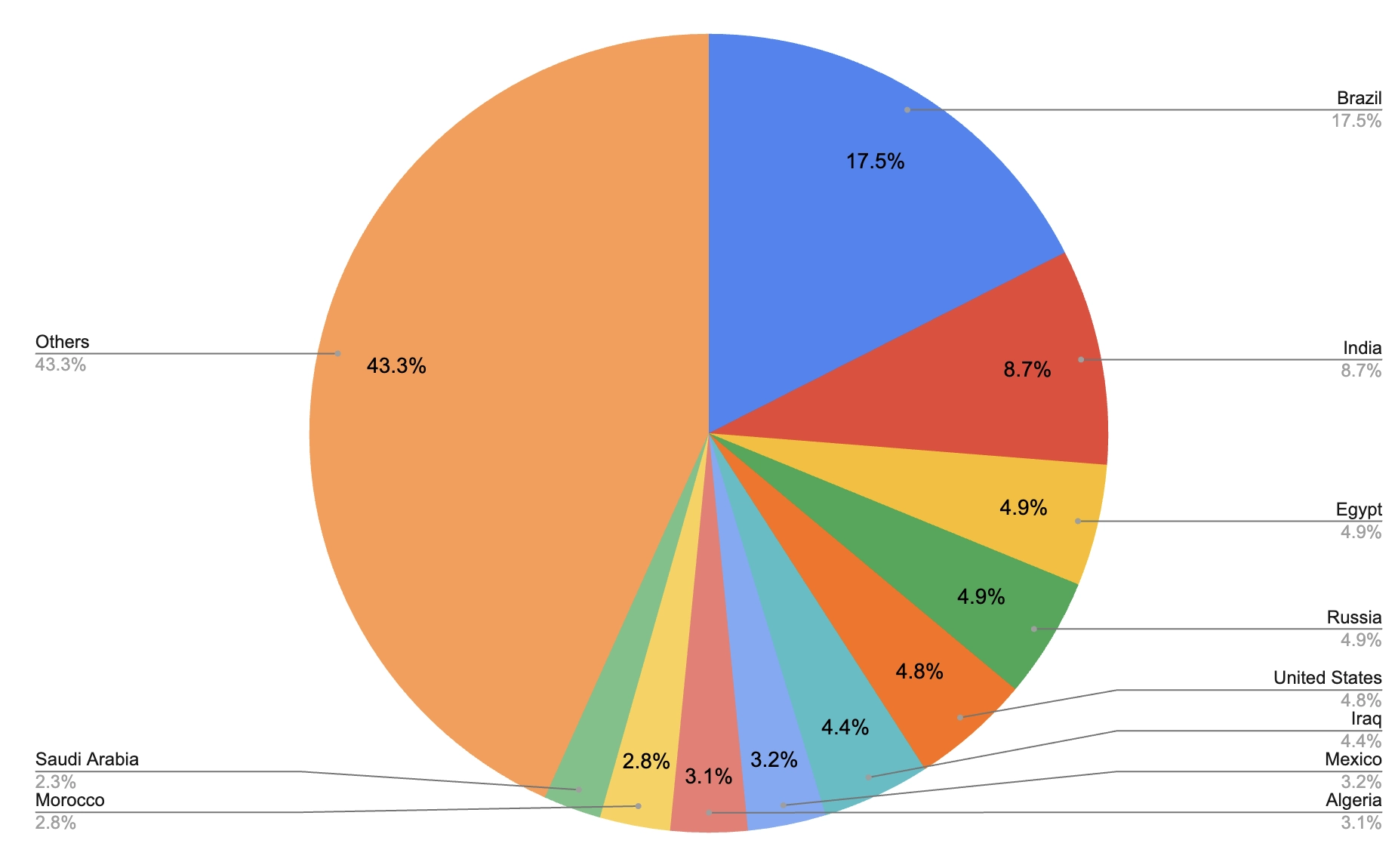
From this data point, we can observe how the Android editor is helping to lower the barrier of entry to game dev by allowing users in Brazil, India, and other countries to make use of cheaper and more accessible Android devices for game development.
Most installs are on phones!
According to the data, ~87% of installs are on phones.
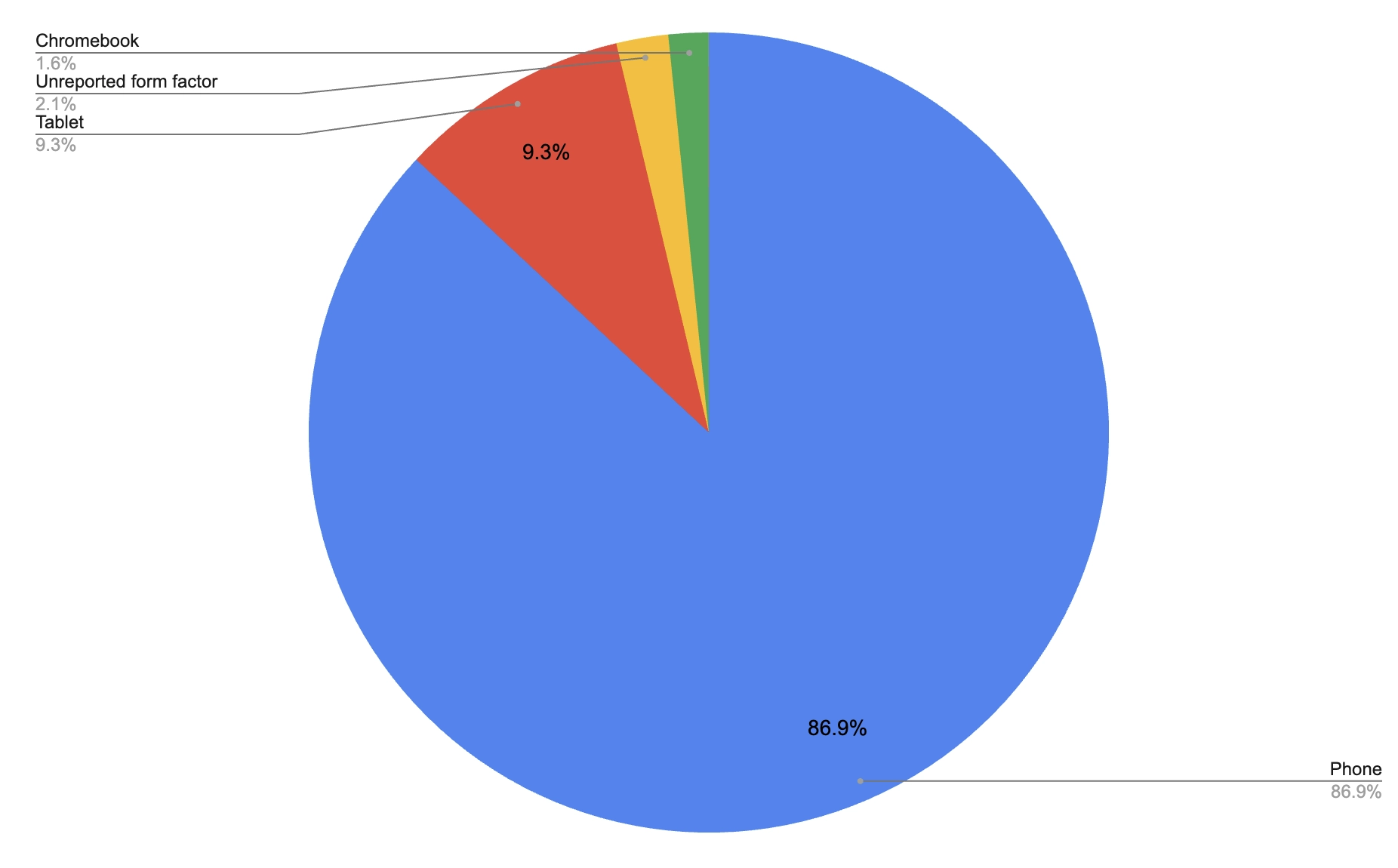
In the Android editor release blog post, we mention it being optimized for large form-factor devices (e.g.: foldables, tablets, Chromebooks), so we expected those types of devices to be driving the installs. However, from the data it can be seen that tablets and Chromebooks only make up ~10.6% of installs. So while the experience is still unoptimized for phones, for a vast number of users, the Android editor has a valuable use and addresses a valid need on regular Android phones.
These data points are driving some of our upcoming work, as in future releases we’ll strive to close the feature parity gap between the Android and desktop versions of the editor, as well as work to improve the Android editor development experience on small form-factor devices like phones.
XR editor
Released in 2024 to great reception, the XR editor is available on the Meta Horizon store and on Godot’s download page with support for Quest 3, Quest 3S, and Quest Pro devices.
To date, the Godot XR editor is the only full game engine running entirely on standalone XR devices and providing users with the ability to develop apps and games with nothing but a standalone XR device. To highlight that fact, David & Logan recently completed a game jam using nothing but the XR editor!
Last fall during GodotCon 2024, the XR editor had ~4K device installs shortly after release. By GodotCon (Boston) 2025, device installs have grown to ~18.5K with ~2000 monthly active users.
We have a lot planned to improve the user experience in order to make the XR editor a powerful, flexible tool for XR and game development, but first we need to improve the reach of the XR editor and make it cross-platform.
To that end, we are working to bring the Godot XR editor to Pico devices.

Early alpha builds can be found on our GitHub release page with support for both Pico 4 and Pico 4 Ultra devices.
We’ve heard loud and clear the feedback and requests for Quest 2 support, and thanks to recent performance improvements courtesy of W4 Games, we’re adding official support for Quest 2 devices as well. You can now download the XR editor to your Quest 2 devices straight from the Meta Horizon store!
Hybrid Apps
Introduced in late 2023, Hybrid Apps are apps that can run both in Panel mode or in Immersive mode, and are able to transition between both modes at runtime. In Panel mode, the app can run side-by-side with other apps, allowing users to multitask. While in Immersive mode, the app’s experience is the sole focus and the user is fully immersed in it.
The feature provides developers with several benefits:
- Developers can easily add immersive support to existing apps and games
- Developers can leverage existing codebase and logic
- Users can select the interaction mode they’re most comfortable with
The Godot XR editor is itself a Hybrid App and has been able to leverage this feature to provide a unique development experience, allowing developers to transition back and forth between the editor window and their immersive projects. With the release of version 4 of the Godot OpenXR Vendors plugin, we’re bringing the same capabilities to all developers in Godot 4.4.
By leveraging v4 of the Godot OpenXR Vendors plugin, developers can build Hybrid Apps straight from the Godot editor. The feature supports all HorizonOS (Quest) devices, with support for Pico devices coming soon!
The feature dynamically enables or disables itself based on the target platform. For example, the same Godot project can run as a regular (panel) app when exported to regular Android devices. And it can run as a full Hybrid App when exported to standalone XR devices.
This allows developers to target multiple audiences, multiple platforms (Android, HorizonOS, PicoOS), and multiple stores (Google Play store, Meta Horizon store, Pico store) with the same project.
To learn more about the feature, please check out the documentation.
Integrating with Android APIs
The Android platform has numerous APIs as well as a rich ecosystem of third-party libraries with wide and diverse functionality. Godot has long provided an Android plugin system which enables developers to create a Godot interface in order to access and use Android APIs or third-party libraries in their projects.
Writing an Android plugin however requires knowledge of Java or Kotlin code, which most Godot developers do not have. As such there are many Android APIs and third-party libraries that don’t have a Godot plugin that Godot developers can interface with. In fact, this is one of the main reasons that developers cite for not being able to switch to Godot from other game engines.
To address this, we’ve introduced a couple of tools in Godot 4.4 to simplify the process for developers to access Android APIs and third-party libraries.
JavaClassWrapper and AndroidRuntime plugin
JavaClassWrapper is a Godot singleton which allows for creating instances of Java and Kotlin classes and calling methods on them using only GDScript, C#, or GDExtension.
AndroidRuntime plugin is a built-in Godot Android plugin that provides access to various Android lifecycle and runtime objects.
Coupling the two together allows developers to access and use Android APIs without switching away from GDScript, or using any tools aside from Godot itself.
This is huge for the adoption of Godot for Android development, as it allows developers to quickly integrate Android functionality without having to make a Java or Kotlin plugin!
For example, this code snippet is all that developers need to access and use the Android Vibrator system service:
# Retrieve the AndroidRuntime singleton
var android_runtime = Engine.get_singleton("AndroidRuntime")
if android_runtime:
# Retrieve the Android Vibrator system service and check if the device supports it
var vibrator_service = android_runtime.getApplicationContext().getSystemService("vibrator")
if vibrator_service and vibrator_service.hasVibrator():
# Configure and run a VibrationEffect
var VibrationEffect = JavaClassWrapper.wrap("android.os.VibrationEffect")
var effect = VibrationEffect.createOneShot(500, VibrationEffect.DEFAULT_AMPLITUDE)
vibrator_service.vibrate(effect)
To learn more about these new capabilities, please check out the documentation.
And more!
There’s plenty more we covered in our GodotCon talk. For the full content, please check out the video and the slides.
Many thanks to the Boston Game Dev and the Boston Godot Users Group for making this event happen.
