Introduction
This is the third part of my work on Complex Text Layouts for Godot 4.0.
See godot-proposals#1180, godot-proposals#1181, godot-proposals#1182, and godot-proposals#1183 on GitHub for detailed information on CTL proposals and feedback.
See also the previous progress report for UI mirroring details and the first part for the TextServer API implementation details.
Changes to the RichTextLabel control
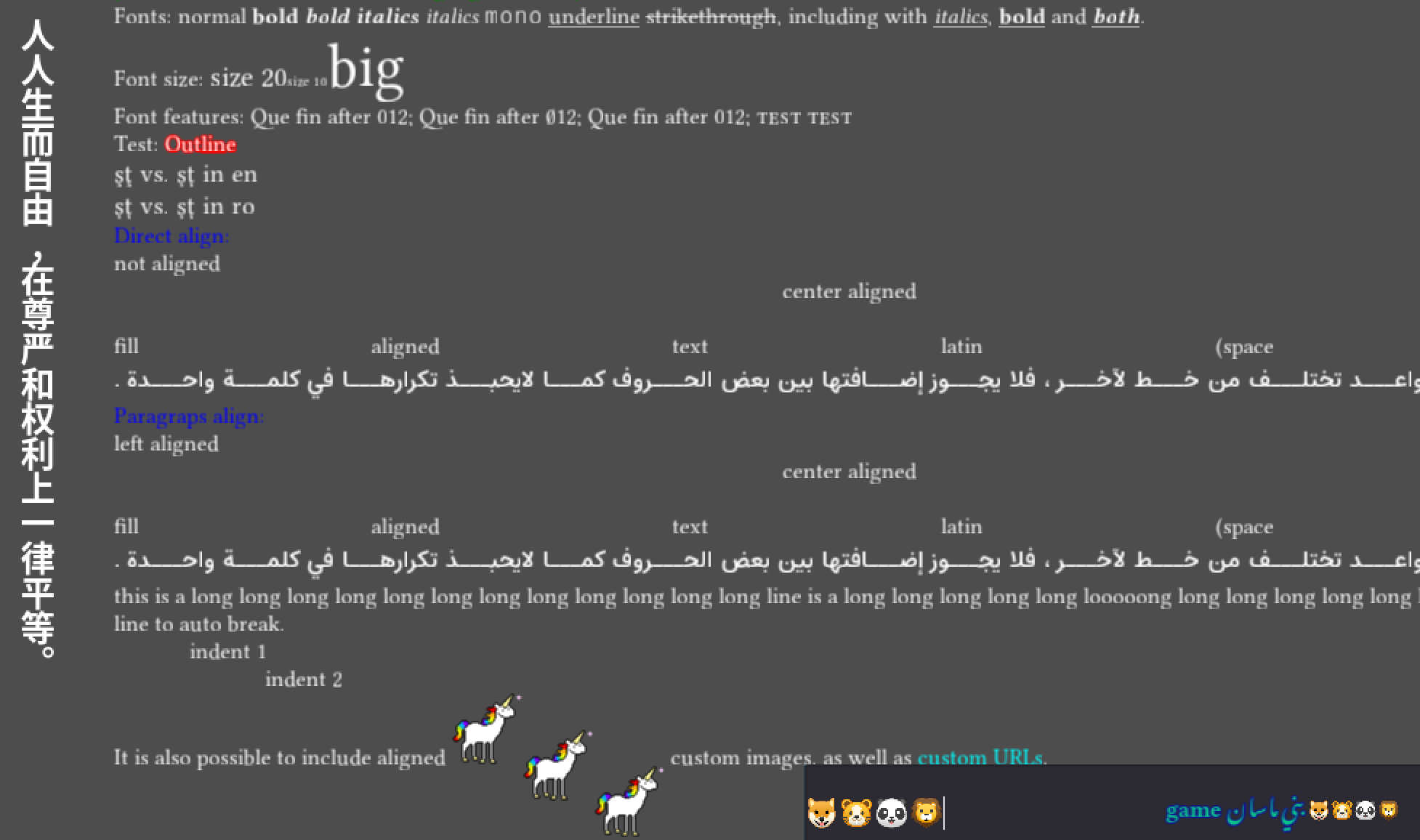
Paragraph
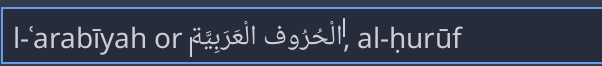
Existing alignment tags ([left], [center], [right], [fill]), as well as new base direction, structured text override and language paragraph options are combined to the single [p] tag. Standalone alignment tags are still available for compatibility.
[p align=x dir=rtl]
| Option | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|
| align | left, center, right, fill | Text alignment. |
| dir or direction | ltr, rtl or auto | Base text writing direction. |
| lang or language | ISO language code | Text language. |
| bidi_override | default, url, file, email, list, none, custom | Structured text BiDi override for the paragraph. |
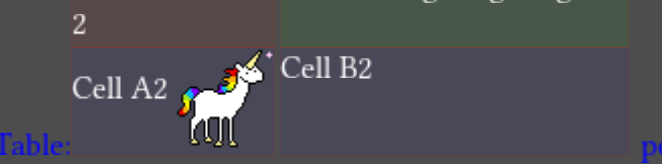
Tables
Support for setting cell background and border colors, including alternating odd/even row background has been added to the table. Table horizontal layout is mirrored for RTL paragraphs.
[cell bg=odd_color,even_color border=color]AAA[/cell]
Additionally, tables can be directly included into the text flow. Table opening and closing tags won’t start a new line anymore.
Lists
Support for numbered and unnumbered lists (list tags existed before but were non-functional) has been added.
[ol type=1]Item 1
Item 2
Item 3[/ol]
The following list types are supported:
- Unnumbered lists (
[ul]). - Numbered lists (
[ol]) using numbers:1type (supports localized numbering systems, e.g. east Arabic numerals, based on paragraph language). - Numbered lists (
[ol]) using Roman numerals:iandItype. - Numbered lists (
[ol]) using Latin letters:aandAtype.

Images
Added support for image inline vertical alignment:
[image align=top]
Font and outline
Added tags to control font size, OpenType features and font outline parameters:
[font_size=36]
[opentype_features=scap]
[outline_color=red][outline_size=2]
or combined in the single tag:
[font name=res://font.tres size=36 features=scap]

Control characters
Unicode control characters can be inserted to the text by inputting them directly (e.g. copy-pasting or using Godot input control context menu), or by using special tags (e.g. [rlm], [lrm], [zwnj]).
Dropcaps
Additionally, dropped capitals support is added to the RichTextLabel. Dropcaps support the same formatting options as the main text, and margins for precise placement control.

Designing custom controls
In addition to the text server interface and draw function in the Font class, TextLine and TextParagraph helper classes, which serve as the base for most Godot controls, are available for more convenient single and multiline text rendering and designing custom controls.
TextLine and TextParagraph classes support the following features:
- Multiple fonts and font options, and multiple languages in the single line or paragraph. Spans of text with designated font and properties can be sequentially pushed to the text buffer.
add_string(text, font, font_size, opentype_features, language) - Text buffers can embed user defined custom objects (e.g. images and tables, like
RichTextLabeldoes) into the text flow. In the text, such objects are represented aslengthobject replacement characters, and follow all BiDi reordering rules. Text buffers handle object size, alignment and placement in the text, drawing and interaction should be implemented separately.add_object(key, size, inline_align, length)The final object position in the text layout can be retrieved by using
get_object_rect(key)function.
Both TextLine and TextParagraph provide direct access to the text server buffer RIDs to mix their usage with direct text server API calls (e.g. accessing individual glyphs).
Text server buffers, TextLine and TextParagraph use a lazy calculation model. No BiDi reordering, shaping, line breaking or any other kind of text processing is done until it’s necessary to do it for the get_* function call or buffer rendering. While layout text is immutable and can’t be changed without redoing BiDi reordering and reshaping, layout size and alignment as well as embedded object sizes can be changed dynamically. Doing so is much faster than new buffer creation.
Limited vertical text support
While Godot controls are designed to work with horizontal text only, text server and TextLine/TextParagraph classes have limited vertical text support as well. Vertical layouts can be enabled by setting the orientation property of the text buffer or helper class.

Input
Godot’s BiDi caret movement follows the logical order of characters (right arrow key always acts as movement forward). If the caret is located on the edge of RTL and LTR text segments, two carets are displayed. Each one indicating a position where newly inputted RTL and LTR characters will be displayed. The primary caret, which controls scrolling, is determined based on the direction of the last inputted character (or can be switched manually, by using Ctrl/Cmd + ~).
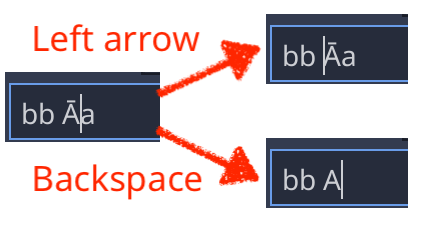
By default, all input keys except Backspace, which always deletes a single character, move the caret over the whole grapheme (i.e. base character and combining diacritics):
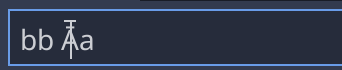
This behavior can be changed by setting mid_grapheme_caret control property:
Note: depending on the OS and language and keyboard layout, some characters can be entered both as combining characters and single characters. In case of single character input, both backspace and movement will affect the whole character.
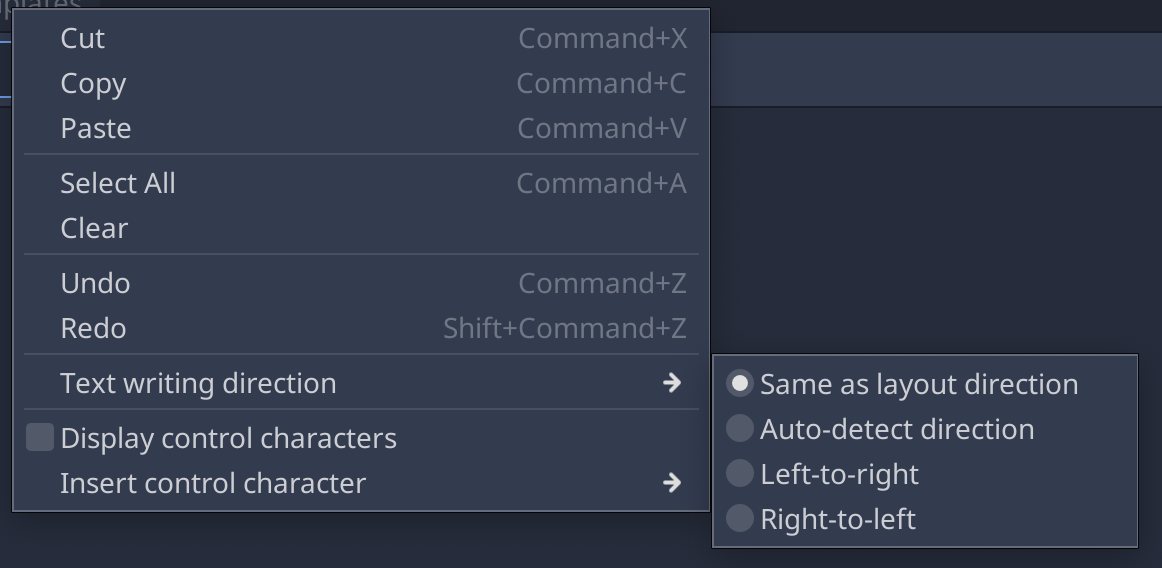
Input controls have various BiDi options available for the user via the context menu:
- Base direction.
- Inserting control characters.
- Enabling and disabling display of control characters.
For the custom controls, the text server provides functions to determine caret positions, selection bounding rectangles and hit testing:
shaped_text_get_carets(RID p_text_buffer, int p_position)
shaped_text_get_selection(RID p_text_buffer, int p_start, int p_end)
shaped_text_hit_test_position(RID p_text_buffer, float p_coord)
All input controls fully support structured text BiDi overrides, which do not interfere with caret movement, do not affect contents of the underlying raw string and unlike Unicode control characters can’t be accidentally modified by the user.
Compatibility
While there are breaking changes in the Font and Theme, existing 3.2 scenes can be loaded directly, some of the conversions will be done automatically:
DynamicFont and BitmapFont resources are converted to the new unified Font resources, but font size will be lost, and should be re-added in the theme properties of the controls.
Font loading and text drawing GDScript code should be changed manually:
- Font loading: Change
DynamicFonttoFont,DynamicFontDataandBitmapFonttoFontData, use single list of data sources. - Text / character drawing and size measurement functions: new arguments for font size, outline and text alignment were added, as well as new function for drawing multiline text.
ICU data, build options and export templates
Full-blown CTL support is slower and results in a bigger binary size. Since some game project do not need CTL at all, or text usage is very limited, multiple compile options are available to control text server building.
The following build options are available:
builtin_graphite, builtin_harfbuzz and builtin_icu (default value: True) - If true, uses built-in version of the libraries instead of system copies (can be disabled for Linux distribution packages).
There are two text server implementations available by default:
ICU, HarfBuzz and SIL Graphite 2 based text server with the full complex text layout support (adv).
Fallback text server without CTL support, it uses same text server API and provides roughly the same text rendering capabilities as in Godot 3.2 (fb).
Text servers can be enabled/disabled by using following build options: module_text_server_adv_enabled, module_text_server_fb_enabled.
If an editor or export template is built with the multiple text servers enabled, the default one can be selected in Project Settings or by using the --text-driver Name command line argument.
At runtime, the text server can be changed by using the TextServerManager class, but doing so will cause all existing fonts and text buffers to become invalid. It’s the user’s responsibility to free all such resources before switching text server.
Additional text servers can be implemented as C++ modules or GDNative libraries, and loaded / used in the same way default servers are.
Some languages do not use spaces between words, and dictionaries (or other type of rule-based word breaking data) are required for better line breaking. ICU provides such data, but its size can be substantial for smaller projects. To reduce export size, ICU data is not included by default, but it can be added at export and stored in the PCK archive. ICU data is always embedded in the editor binaries. Also, you can avoid the necessity for ICU data at all by manually adding valid breaking points (by adding zero-width breaking spaces, which can be inserted from Godot input controls’ context menu).
Demos and docs
- CTL documentation and tutorials PR - https://github.com/godotengine/godot-docs/pull/4319
- CTL demos PR - https://github.com/godotengine/godot-demo-projects/pull/538
Reference work
- UI improvements for implementing BiDi aware apps proposal - https://github.com/godotengine/godot-proposals/issues/1183
- CTL implementation main PR (merged) - https://github.com/godotengine/godot/pull/41100
- RichTextLabel control refactoring PR (merged) - https://github.com/godotengine/godot/pull/42595
- Variable font support PR (merged) - https://github.com/godotengine/godot/pull/43030
- Compatibility support for the legacy Font resources PR (merged) - https://github.com/godotengine/godot/pull/43931
- Drop cap support PR (merged) - https://github.com/godotengine/godot/pull/43691